42 identify the parts of the sun labeled
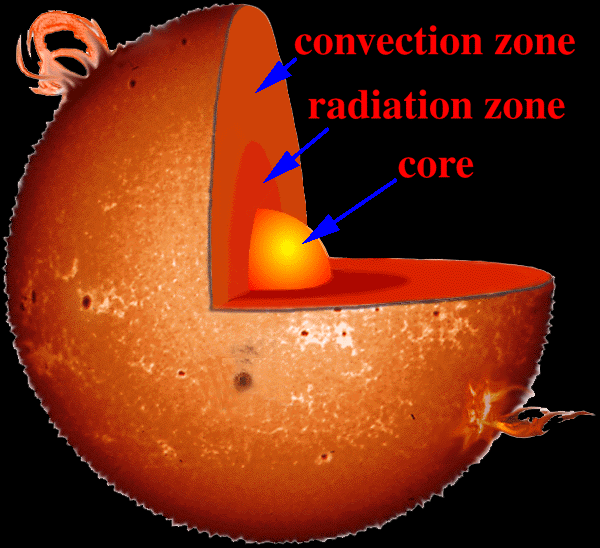
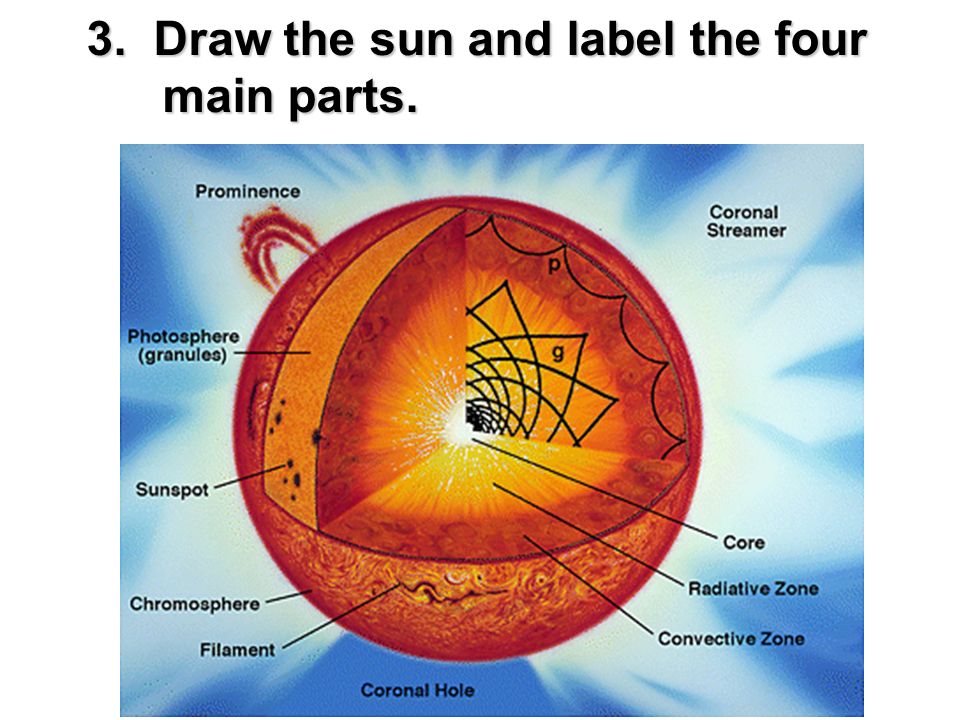
Layers of the Sun | Parts of the Sun | DK Find Out Inside the sun. The structure of the sun is made up of four layers. At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere. Regions and Features of the Sun | Center for Science Education The visible "surface" of the Sun, called the photosphere, sits atop the interior layers. The Sun also has an atmosphere, with a lower region called the chromosphere and an upper section known as the corona. Numerous features, with lifetimes of seconds to months, appear on the Sun's surface and in the solar atmosphere.
Diagram of the Parts of a Flower - Sciencing The stamen is the male part of a flower. In a flower diagram, stamen are located on both sides of the pistil. The stamen consists of two parts: Anther: The anther is the head of the stamen. It produces pollen. Filament: The filament is the stalk attached to the flower that holds the anther. The stamen's function is to produce male reproductive ...

Identify the parts of the sun labeled
Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Biology High School answered Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Advertisement Answer 4.1 /5 11 368esc07 Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIATIVE ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE Layer E- CHROMOSPHERE Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. Layer E - Corona Earth's rotation around the Sun and the sequence of four seasons The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365 and quarter days (one year), The rotation of the Earth around the Sun causes the sequence of the four seasons (the summer - the spring - the autumn - the winter). The sequence of the four seasons. The Earth's axis is inclined and this causes the difference in the length of the day and the ... Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label E Expert-verified answer throwdolbeau Answer: Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIATIVE ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE Layer E- CHROMOSPHERE Explanation: The core of the sun is the interior past where nuclear reactions leads to the consumption of hydrogen gas in order to form helium gas.
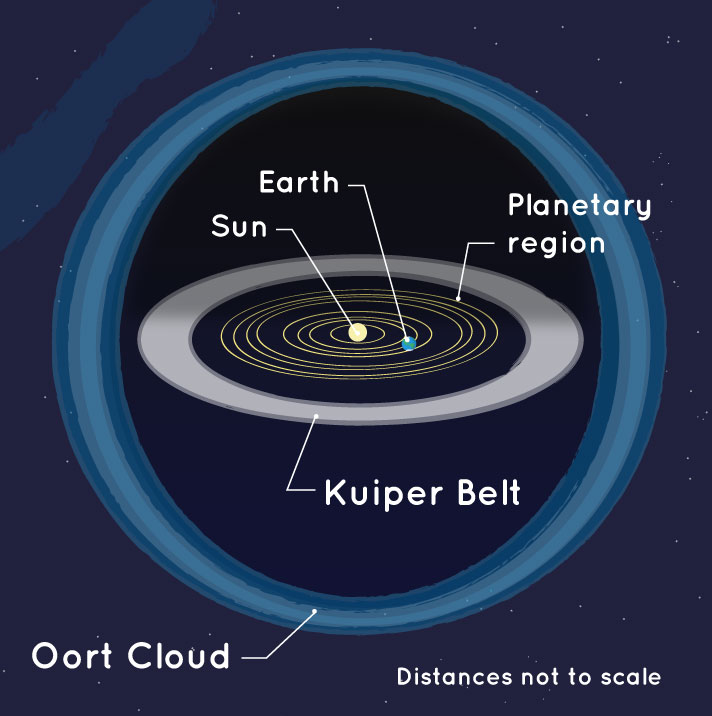
Identify the parts of the sun labeled. Sun Lessons, Worksheets and Activities - Teacherplanet.com The sun is the center of our solar system. It's a star, an extremely large star, which is about 109 times the size of the Earth. Scientists estimate that the sun formed about 4.57 billion years ago. Since the beginning of time, humans have attributed much significance to the sun. It's been the center of religions, mythology and of course, it ... Parts of the Ellipse with Diagrams - Mechamath The two fixed points are called the foci of the ellipse. The foci are surrounded by a curve that has an oval shape. Some of the most important parts of ellipses are the center, the foci, the vertices, the major axis, and the minor axis. Here, we will learn more details of the parts of the ellipse along with diagrams to illustrate the concepts. NASA - Layers of the Sun The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona. IRIS will focus its investigation on the Chromosphere and Transition Region. More detail on the outer layers follows: Photosphere- The photosphere is the deepest layer of the Sun that we can observe directly. Parts of the Sun Flashcards | Quizlet Photosphere. Lowest layer of the Sun's atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000K. Chromosphere. Layer of the Sun's atmosphere above the photosphere. Prominence. Links different parts of the sun spot regions together. Corona. Layer of the Sun that is only visible during a solar eclipse.
Layers of the Sun Flashcards | Quizlet Photosphere. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light. Solar Wind. a stream of charged particles produced by the corona. Prominence. Reddish loops of gas that link parts of sunspot regions. Radiation Zone. the layer of the sun's interior where energy is transferred mainly by electromagnetic radiation. Convection Zone. The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. PDF The Sun Worksheet - Northland Preparatory Academy a. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light b. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that has a reddish glow c. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that looks like a halo during an eclipse d. areas of gas on the sun's surface that are cooler than the gases around them e. reddish loops of gas that link parts of sunspot ... Layers of the Sun - The Sun Today with Dr. C. Alex Young The Sun, as shown by the illustration to the left, can be divided into six layers. From the center out, the layers of the Sun are as follows: the solar interior composed of the core (which occupies the innermost quarter or so of the Sun's radius), the radiative zone, and the convective zone, then there is the visible surface known as the photosphere,
The sun's atmosphere: Photosphere, chromosphere and corona The sun's photosphere is the innermost layer of the sun that we can observe directly. (Image credit: NASA/SDO) (opens in new tab) The photosphere is the lowest layer of the sun's atmosphere ... How the Sun Works | HowStuffWorks The Sun Is Also a Star. The sun is a star, just like the other stars we see at night. The difference is distance -- the other stars we see are light-years away, while our sun is only about 8 light minutes away -- many thousands of times closer. Officially, the sun is classified as a G2 type star, based on its temperature and the wavelengths or spectrum of light that it emits. What Are The Layers Of The Sun? - WorldAtlas The layers of the Sun are divided into two larger groups, the outer and the inner layers. The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. There are four outer layers of the Sun, and the Corona is the outermost one. Solved Identify which parts of the globe experience the | Chegg.com Lastly, in order to calculate the SAA, simple subtract the zenith angle from 90°. Remember that the SAA is an angle, so do not label the SAA with North or South. Example: Las Vegas, Nevada (36°N) on December 21 (23.5°S solar declination) Zenith angle = 36° - (-23.5°) Zenith angle = 36° + 23.5°. Zenith angle = 59.5°. SAA = 90° - 59.5°.
Layers of the Sun - Science Facts Corona: The Outer Layer The outermost layer is the corona and can be seen during a solar eclipse when the sun is blocked by the moon. This layer is hotter than the surface of the sun. Less Than Five - Layers of the Sun Explained - Outer Layers Watch on The sun has many chemical elements but since it is so hot they are in a gaseous state.
15.1 The Structure and Composition of the Sun - OpenStax This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Labelling the Sun For the exercise below, identify each of the parts of ... Although only visible during a solar eclipse, the chromosphere is red in color. 6 Corona The tenuous uppermost layer of the sun's atmosphere; most of the suns X rays are emitted from this region, in which the temperature is about 1 million K. the corona cannot be seen with the naked eye 7 Sun spots Blotches on the surface of the sun that appear darker than surrounding regions 8 Granule The bubbling pattern visible in the photosphere, produced by the underlying convection 9 Prominence A ...
PDF The Structure of the Sun - Space Weather Prediction Center The Sun's interior domain includes the core, the radiative layer , and the convective layer (Figure 2-1). The core is the source of the Sun's energy, the site of thermonuclear fusion. At a temperature of about 15,000,000 K, matter is in the state known as a plasma: atomic nuclei (principally protons) and electrons moving at very high speeds.
What are the Parts of the Sun? - Universe Today If you could take the Sun apart, and stack up its various elements, you would find that the Sun is made of hydrogen (74%) and helium (about 24%). Astronomers consider anything heavier than helium...
The Sun - Imagine the Universe! The Sun. The Sun is a star, just like the ones you can see in the night sky, but much, much, much closer. In fact, our Sun is a rather ordinary star - it's not particularly big or particularly small, it's not particularly young or particularly old. Just an ordinary, run-of-the-mill star. However, since it is so close to Earth, it is the one ...
What Are the Parts of the Periodic Table? - ThoughtCo All elements in a group share the same number of valence electrons. The three broad categories of elements are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are metals. Nonmetals are located on the righthand side of the periodic table. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals. 3 Main Parts of the Periodic Table
Layers of the Sun | NASA Chromosphere - The chromosphere is a layer in the Sun between about 250 miles (400 km) and 1300 miles (2100 km) above the solar surface (the photosphere). The temperature in the chromosphere varies between about 4000 K at the bottom (the so-called temperature minimum) and 8000 K at the top (6700 and 14,000 degrees F, 3700 and 7700 degrees C), so in this layer (and higher layers) it actually gets hotter if you go further away from the Sun, unlike in the lower layers, where it gets hotter if ...
2022 UPDATED!!! Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E ... Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E THIS IS THE BEST ANSWER 👇 Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIO ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE R-CHROMOSFAR layer
Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label E Expert-verified answer throwdolbeau Answer: Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIATIVE ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE Layer E- CHROMOSPHERE Explanation: The core of the sun is the interior past where nuclear reactions leads to the consumption of hydrogen gas in order to form helium gas.
Earth's rotation around the Sun and the sequence of four seasons The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365 and quarter days (one year), The rotation of the Earth around the Sun causes the sequence of the four seasons (the summer - the spring - the autumn - the winter). The sequence of the four seasons. The Earth's axis is inclined and this causes the difference in the length of the day and the ...
Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Biology High School answered Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Advertisement Answer 4.1 /5 11 368esc07 Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIATIVE ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE Layer E- CHROMOSPHERE Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. Layer E - Corona




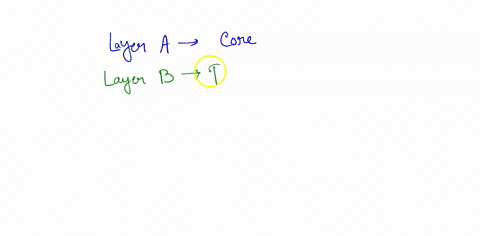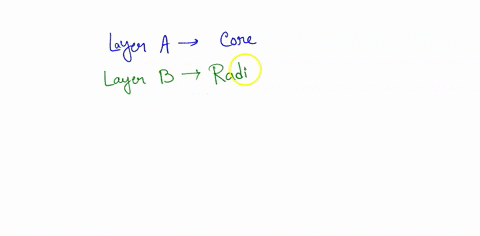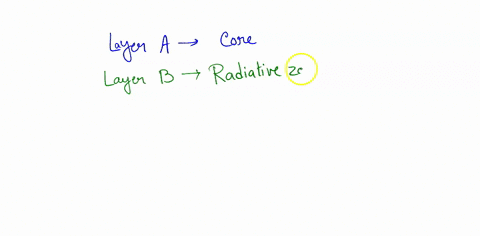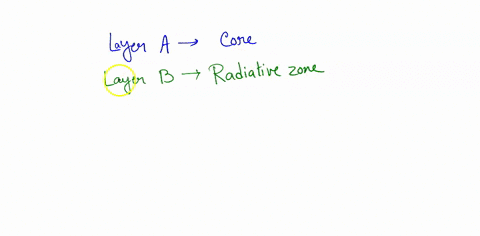



















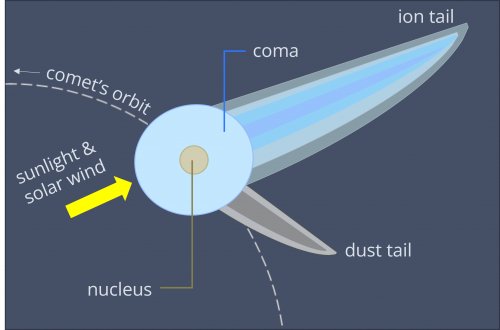




Post a Comment for "42 identify the parts of the sun labeled"