41 parts of the animal cells
Animal Cell - Science Quiz - GeoGuessr Animal cells are packed with amazingly specialized structures. One vital part of an animal cell is the nucleus. It's the cell's brain, employing chromosomes to instruct other parts of the cell. The mitochondria are the cell's powerplants, combining chemicals from our food with oxygen to create energy for the cell. Animal cells - Cell structure - AQA - BBC Bitesize Animal cells have a basic structure. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell, on the left viewed with the light microscope, and on the right with the transmission electron...
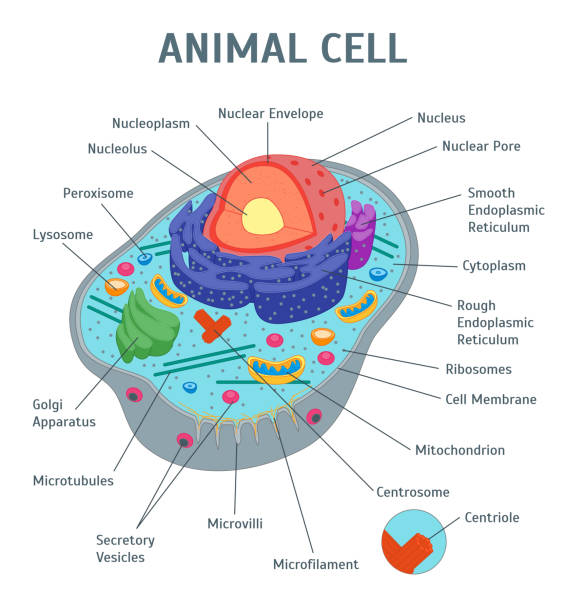
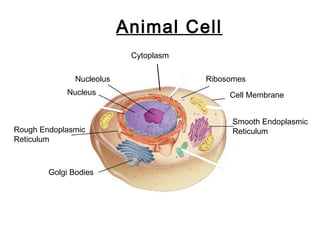
Animal Cells | Basic Biology The cells of animals and plants almost always have a 'true' nucleus. A nucleus consists of a nuclear envelope, chromatin, and a nucleolus. The nuclear envelope is made from two membranes and encapsulates the contents of the nucleus. The double membrane has numerous pores to allow substances to move in and out of the nucleus.

Parts of the animal cells
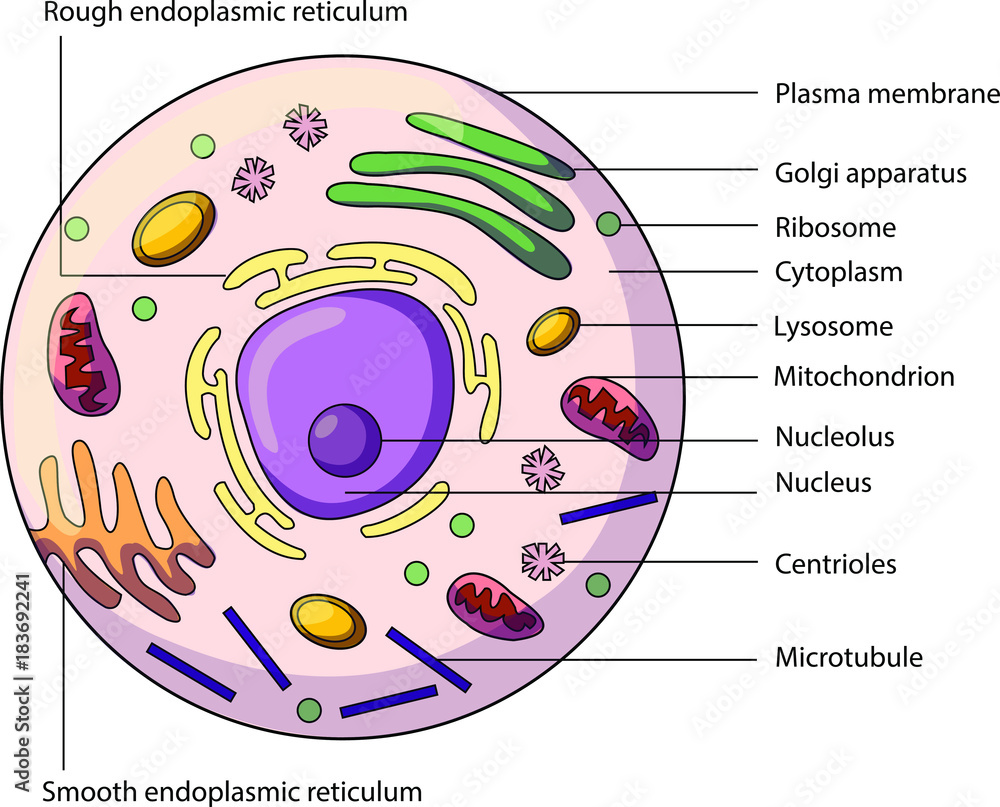
Animal Cell: Animal Cell Diagram: Types, and Functions - Embibe The eukaryotic cells have cell organelles lacking in prokaryotic cells except for the ribosomes. The animal cells consist of the centriole, which carries out cell division. The animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. Along with that, it possesses locomotory structures. What are the parts and functions of an animal cell? THE THREE MAIN COMPONENTS OF ANY PLANT OR ANIMAL CELL ARE: PLASMA MEMBRANE/ CELL MEMBRANE. Structure- a bilipid membraneous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates. CYTOPLASM. NUCLEUS. 1. " RIBOSOMES. GOLGI BODY / APPARATUS. LYSOSOMES. MITOCHONDRIA. What is the primary structure of plant cells? Plant Cell Parts & Functions | What is a Plant Cell? - Study.com The outermost portion of a plant cell is the cell wall. This is also a part that animal cells do not have. The function of a cell wall is to give the cell rigidity and support, as well as allow ...
Parts of the animal cells. Cytoskeletons in Animal Cells Function & Location - Study.com The main cytoskeleton function in animal cells is to provide structure and support. However, there are also many other functions of the cytoskeleton, including: Regulating cell division ... Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all made up of at least one eukaryotic cell. In contrast, bacteria and archaea are made up of a single prokaryotic cell. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane (also called a plasma membrane ). The cell membrane is the boundary that separates the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell. How Does the Animal Cell Work? Learn About the Functioning of a Cell in ... Three Basic Parts of the Cell. The animal cell is made up of three basic parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus and protoplasm. Consider the cell membrane as the gatekeeper. It surrounds the cell contents and separates the cell from other cells and from the external environment. Nothing gets in or out without permission from the nucleus. Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small. Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play several roles: storing nutrients and waste products, helping increase cell size during growth, and even acting much like lysosomes of animal cells. The plant cell vacuole also regulates turgor pressure in the cell.
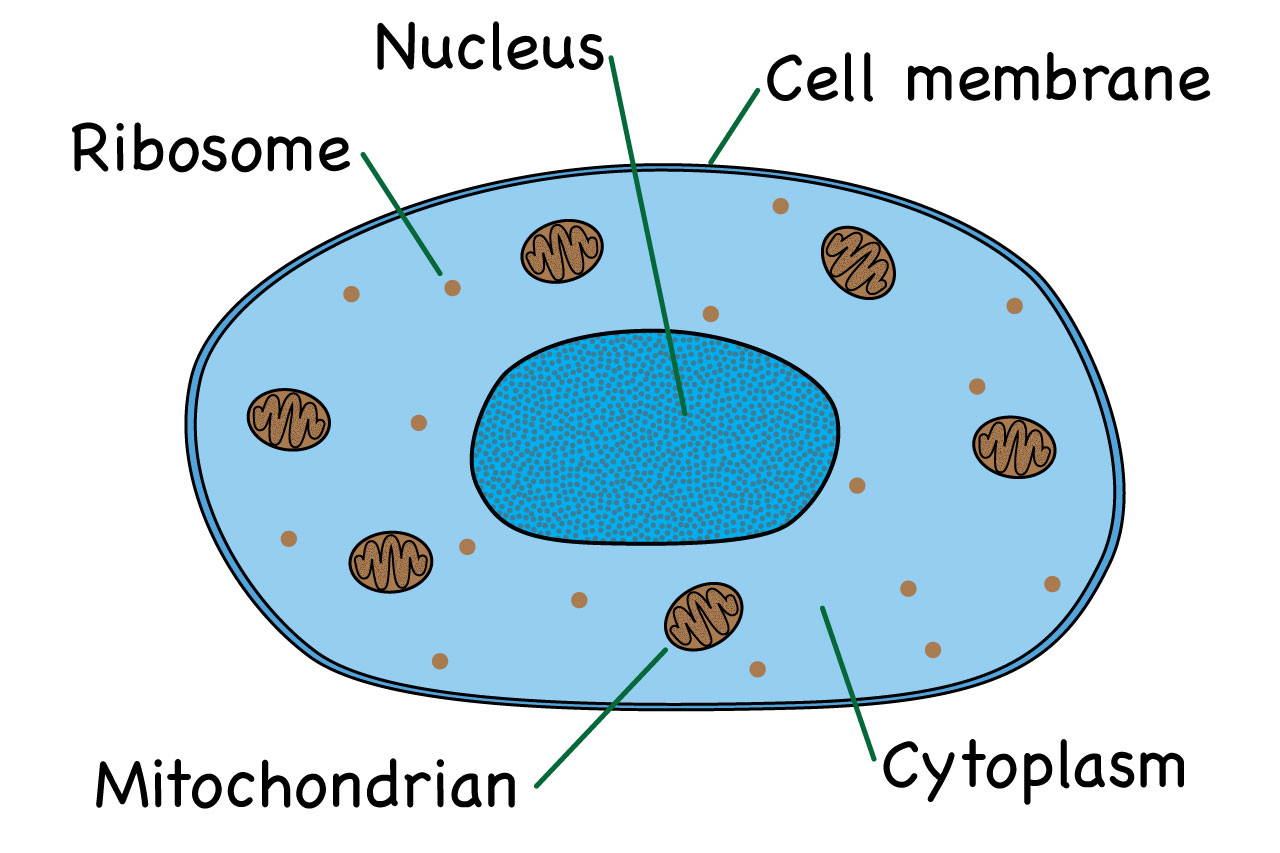
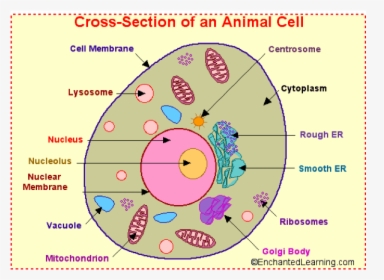
What are cells? Animal and plant cells - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize The four key components of most animal cells are: Nucleus - this contains the genetic material (DNA) of the organism and controls the cell's activities. Cytoplasm - the liquid that makes up most of... Animal Cell - Cells For Dummies - Weebly An analogy of a animal cell is a city. The nucleus can be the city hall because the city hall controls everything in the city and it's just like the nucleus because the nucleus controls want happens in the cell. The vacuole can be a water tower because a water tower stores water and the vacuole also stores water along with a couple of other ... Animal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and Types - BYJUS There are numerous types of animal cells, each designed to serve specific functions. The most common types of animal cells are: Skin Cells Melanocytes, keratinocytes, Merkel cells and Langerhans cells Muscle Cells Myocyte, Myosatellite cells, Tendon cells, Cardiac muscle cells Blood Cells Leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelet Nerve Cells Interactive Cell Models - CELLS alive For life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells.
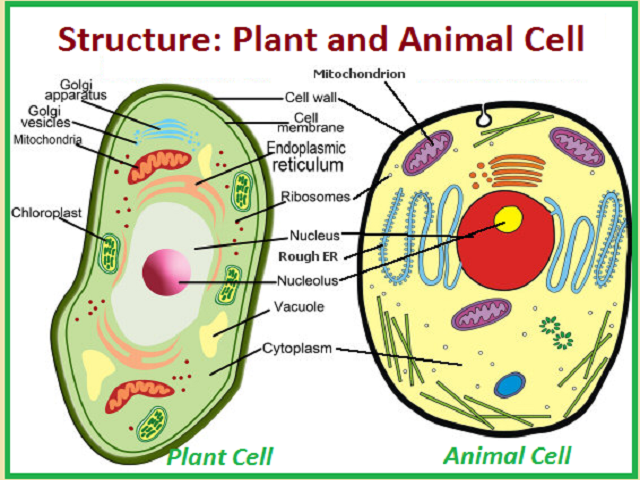
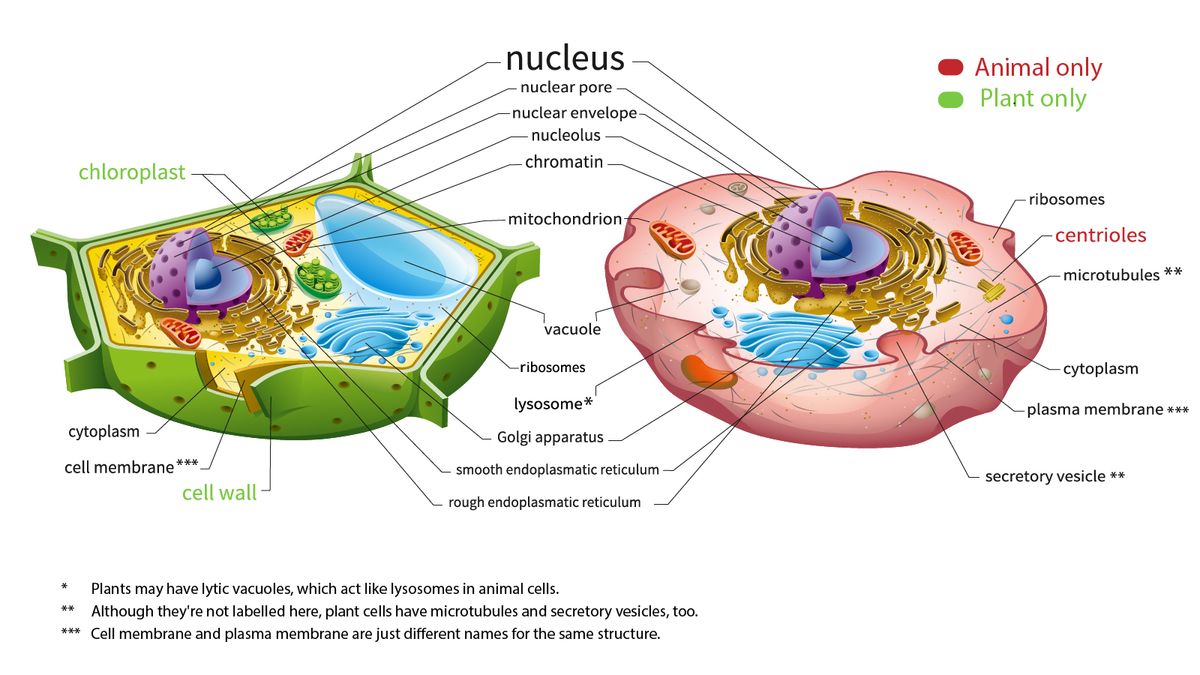
Animal vs. Plant cells - Similarities, Differences, Chart ... Animal and plant cells are eukaryotic cells. They all have nuclei, cell membranes, and organelles (ER, Golgi, ribosomes, and mitochondria). The structures only in plant cells are the cell wall, chloroplast, and vacuole. Biology4Kids.com: Cell Structure There are many types of cells. In biology class, you will usually work with plant-like cells and animal-like cells. We say "animal-like" because an animal type of cell could be anything from a tiny microorganism to a nerve cell in your brain. Biology classes often take out a microscope and look at single-celled microbes from pond water. Plant and Animal Cells - National Oceanic and Atmospheric ... The first difference is a structure known as\ഠchloroplasts, which plant cells have and animal cells do not. Chloroplasts are what give plants their green color. The second對 major difference between plant and animal cells is the cell wall. While both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane, onl\൹ plants have a cell wall. label parts of animal cell - Teachers Pay Teachers 4.9. (33) $1.50. PDF. Google Apps™. Label an animal cell and match the parts with its definition. Answer keys are included for easy grading! A digital version of this resource is also included and is compatible with Google Classroom. You may also like: Biology VocabularyParts of a Plant Cell - Labeling & MatchingParts of an Animal Cell ...
The Complete Guide to Animal Cells - PrepScholar Animal Cell Model and Parts of the Animal Cell. Animal cells contain small structures called organelles, which help carry out the normal operations of a cell. Each of the organelles is essential in making sure the cell functions properly. These are the organelles found in most animal cells:
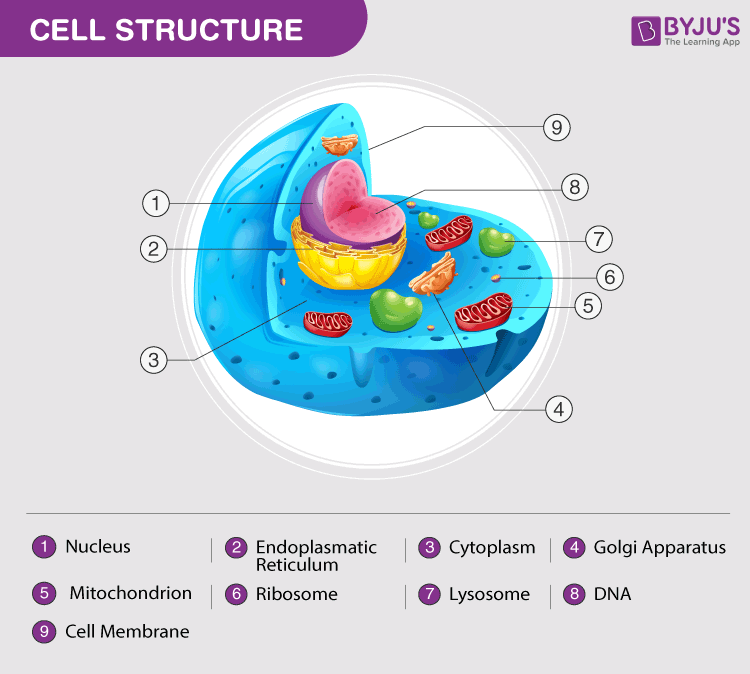
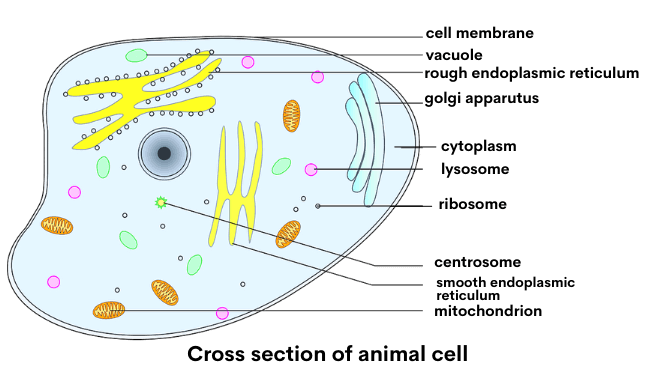
Plant and Animal Cell: Definition, Structure, Differences - Embibe Exams What are the parts of the Animal cell? Ans: Cell Membrane, Nuclear Membrane, Nucleus, Centrosome, Lysosome, Cytoplasm, Golgi Apparatus, Mitochondrion, Ribosome, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Vacuole, Nucleopore, are the parts of the Animal cell. Q.2. What are the parts of the Plant cell?
Animal Cell - Functions and Structure of Animal Cells - VEDANTU In biological terms, an animal cell is a typical eukaryotic cell with a membrane-bound nucleus with DNA present inside the nucleus. It comprises other cellular structures and organelles which helps in carrying out some specific functions required for the proper functioning of the cell.
Animal Cell Parts - Biology Wise Cell wall and chloroplast are present in plant cells, while animal cells do not have cell walls. All the animal cells are not of the same shape, size, or function but the main cellular mechanism is the same which helps in proper functioning of the body. There are various parts which make up an animal cell, so let's get an insight into what ...
Cell parts and functions (article) | Khan Academy Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. A cell's organelles work alone and together to keep the whole cell functioning. Mitochondria are organelles that break down sugars. This process releases energy that the cell can use. The nucleus is an organelle that contains a cell's genes.
Animal Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems - ThoughtCo During the development of an animal, eukaryotic cells differentiate so they can perform specific functions. Groups of cells with similar specializations, and which perform a common function, are referred to as tissues. Organs (examples of which include lungs, kidneys, hearts, and spleens) are groups of several tissues that function together ...
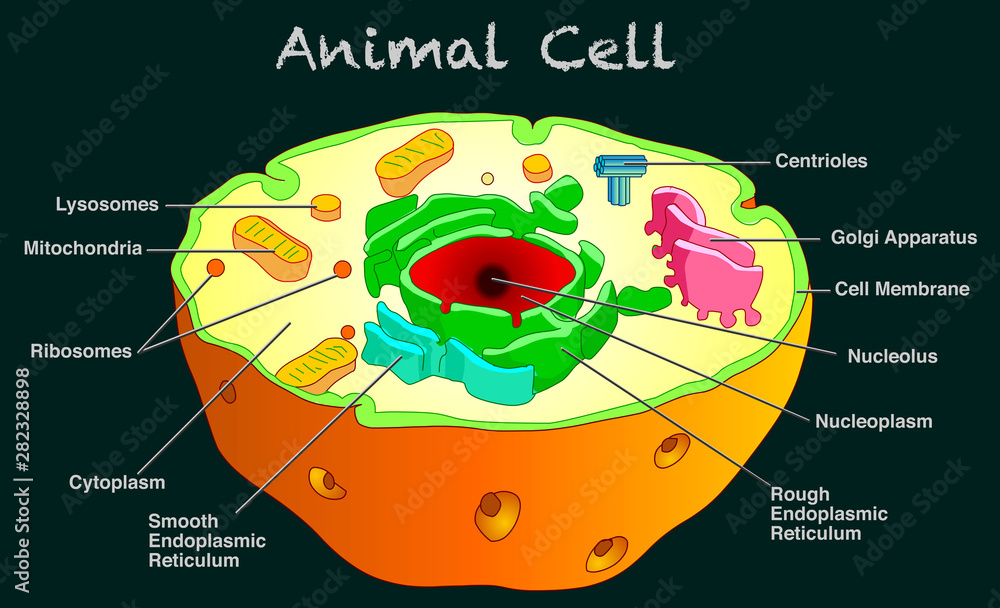
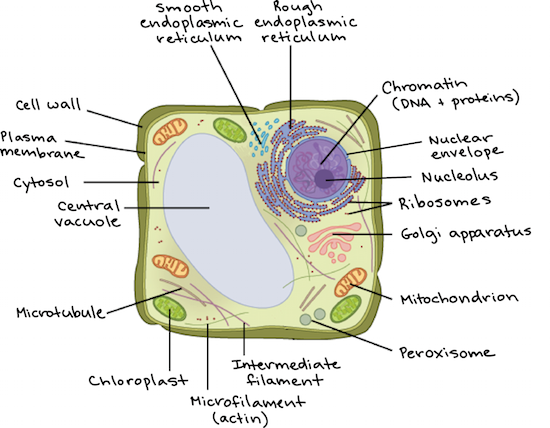
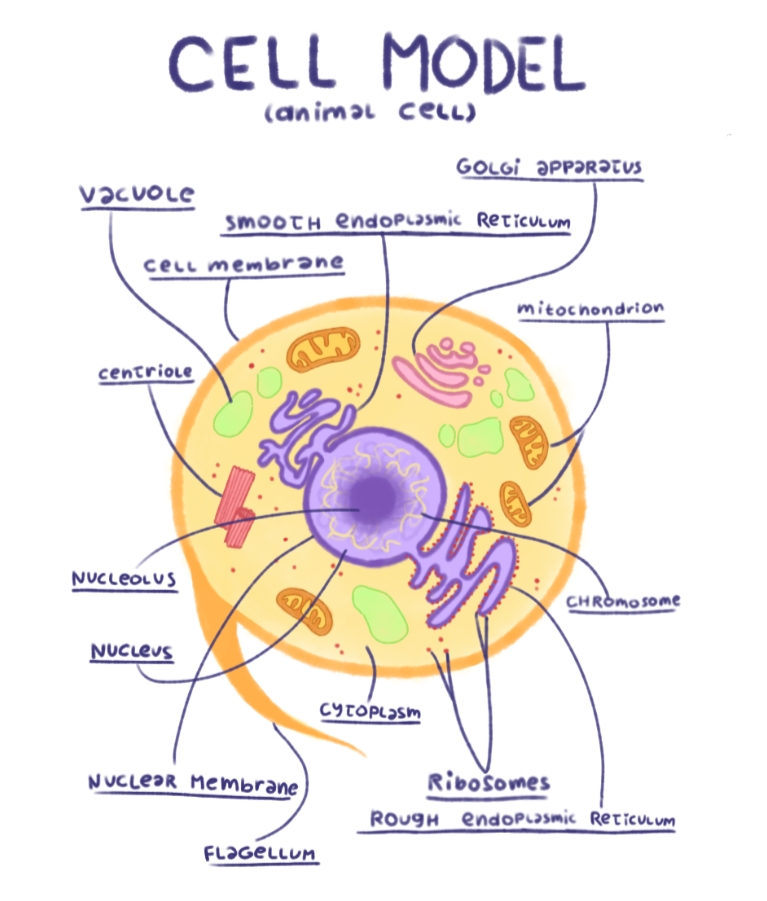
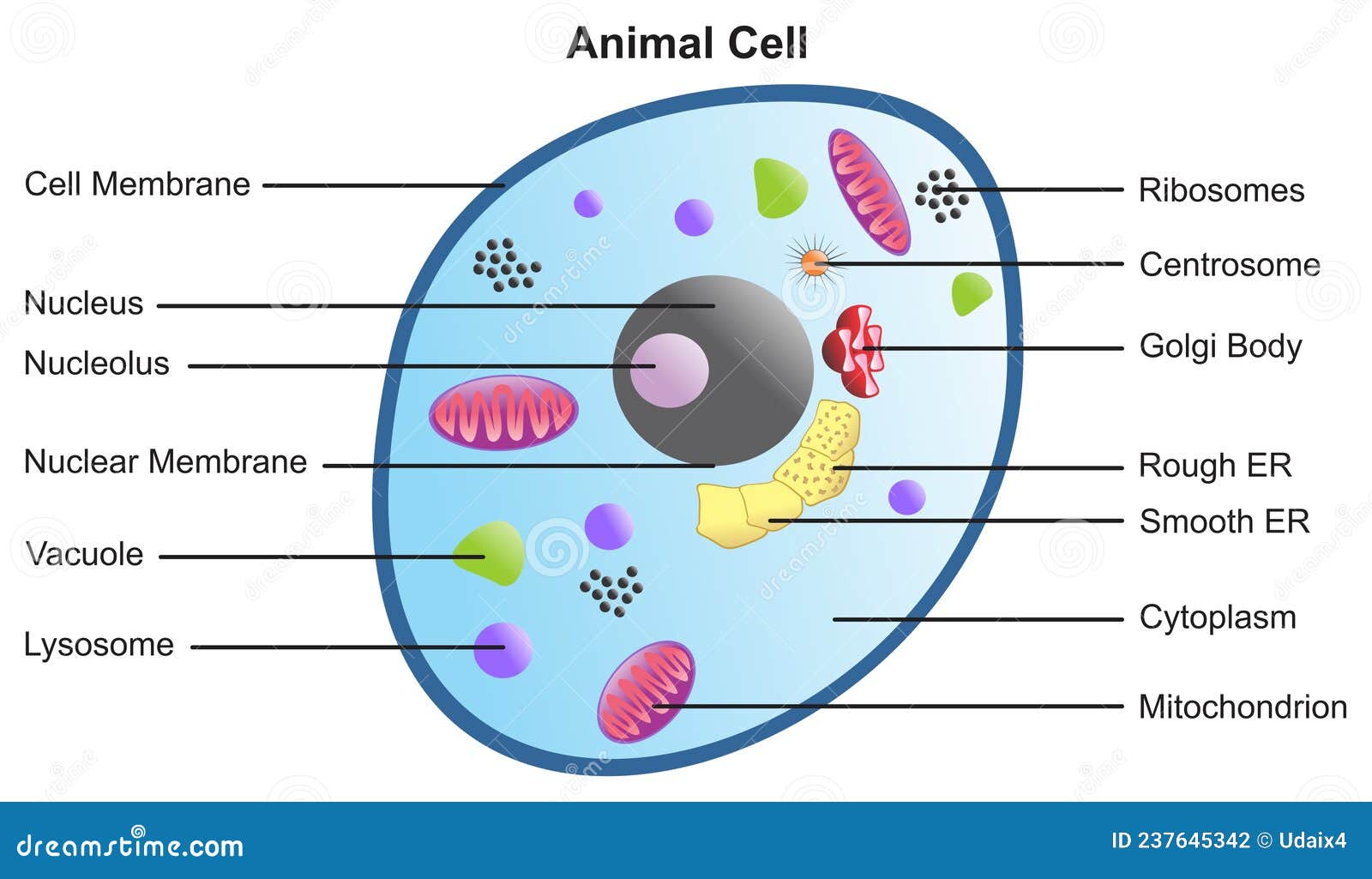
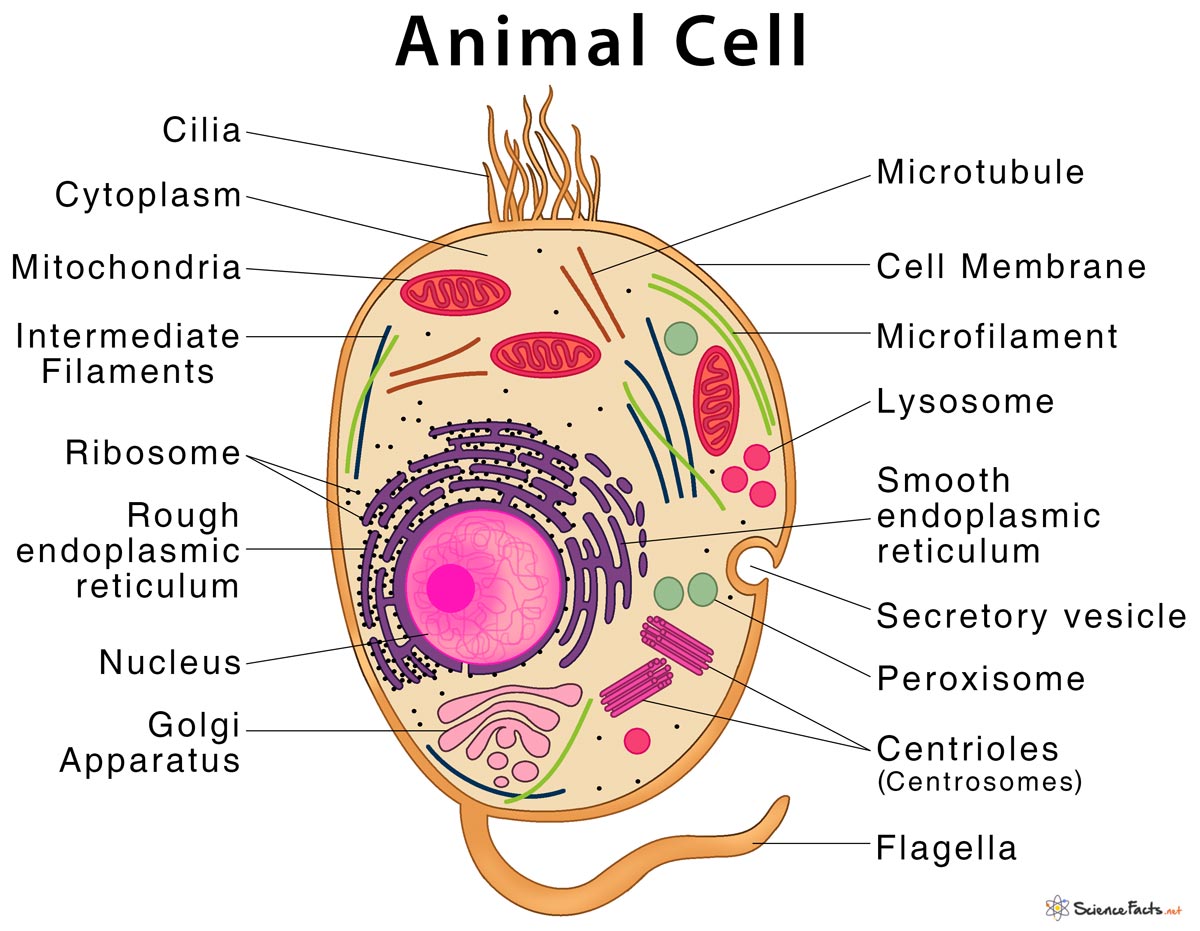
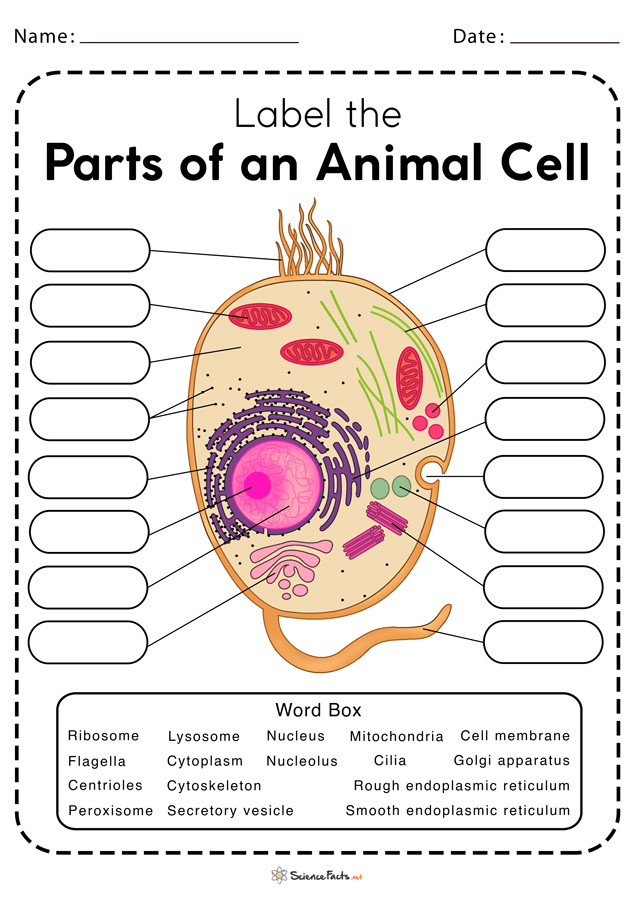
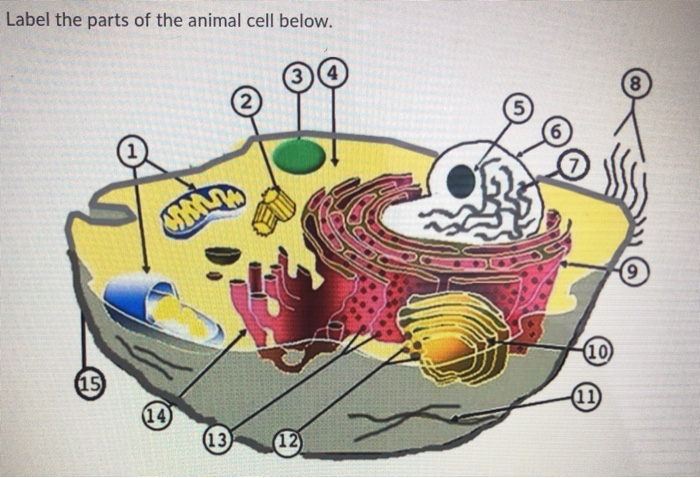
The Parts Of An Animal Cell | Science Trends There are 13 main parts of an animal cell: cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, centrioles, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, and vesicles.
Cells Cells - Parts of the Cell Rap - YouTube This rap was created for a 6th-grade science classroom to teach about the different parts of a cell. With its catchy rhythm and rhymes, students of all learn...
What are the 13 parts of an animal cell? - BYJUS The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus. You can read about the Plant Tissues - Classification, Definition, Types in the given link.
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo Animal cells and plant cells are similar in that they are both eukaryotic cells.These cells have a true nucleus, which houses DNA and is separated from other cellular structures by a nuclear membrane. Both of these cell types have similar processes for reproduction, which include mitosis and meiosis.Animal and plant cells obtain the energy they need to grow and maintain normal cellular ...
What’s the difference? Plant, animal, and bacterial cells These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria (prokaryotic) Have a defined nucleus. Found in organisms made up of many cells. Example: Plant and Animal cells. Structure: Eukaryotic. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall (plant cells only) Centrosome. Centriole (animal cells only) Chloroplast (plant cells only) Cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton. Cytosol ...
What are the parts of an animal cell and its functions? - Quora Main parts of animal cell are cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm and other cytoplasmic organelles such as Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and centrosome. Henry K.O. Norman Retired Programmer, Studying Cell Biology Author has 7K answers and 10.4M answer views 1 y
Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary Plant and animal cells both contain organelles, many of which are found in both types of cells. However, there are some organelles (such as chloroplasts, the cell wall, and large vacuoles) that are only found in plant cells. Plant and animal cells contain subcellular structures called organelles Animal Cell Parts And Their Functions
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. What is Animal Cell? Animals are made of eukaryotic cells having nucleus, cellular organelles, and are surrounded by a cell membrane or plasma membrane. What is Plant Cell? Plant cell are the basic unit of all plants.
What are the Parts of an Animal Cell? - YouTube Learn about all of the parts that make up an animal cell, and their function.We hope you are enjoying this video! For more in-depth learning, check out Miaca...
Animal cell parts and their function - WhatMaster The animal cell is fundamentally composed of a plasma membrane, a nucleus, and a cytoplasm. Next, we will explain each one in detail. Plasma membrane The plasma membrane is the outer covering of the cell, through which contact is made with the external environment. It consists of two sheets of lipids, lipid bilayer, and membrane proteins.
Comparing animal and plant cells (video) | Khan Academy NGSS.MS: MS‑LS1‑2. , MS‑LS1.A.2. Transcript. Plant cells have a cell wall in addition to a cell membrane, whereas animal cells have only a cell membrane. Plants use cell walls to provide structure to the plant. Plant cells contain organelles called chloroplasts, while animal cells do not. Chloroplasts allow plants to make the food they ...
Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram List of Animal cell organelles Plasma membrane (Cell membrane) Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex) Lysosomes Cytoskeleton Microtubules Centrioles Peroxisomes Cilia and Flagella Endosome Vacuoles Microvilli Animal cell structure
Plant Cell Parts & Functions | What is a Plant Cell? - Study.com The outermost portion of a plant cell is the cell wall. This is also a part that animal cells do not have. The function of a cell wall is to give the cell rigidity and support, as well as allow ...
What are the parts and functions of an animal cell? THE THREE MAIN COMPONENTS OF ANY PLANT OR ANIMAL CELL ARE: PLASMA MEMBRANE/ CELL MEMBRANE. Structure- a bilipid membraneous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates. CYTOPLASM. NUCLEUS. 1. " RIBOSOMES. GOLGI BODY / APPARATUS. LYSOSOMES. MITOCHONDRIA. What is the primary structure of plant cells?
Animal Cell: Animal Cell Diagram: Types, and Functions - Embibe The eukaryotic cells have cell organelles lacking in prokaryotic cells except for the ribosomes. The animal cells consist of the centriole, which carries out cell division. The animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. Along with that, it possesses locomotory structures.

















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_cell-56c765663df78cfb3788382b-5c2e861046e0fb000142aa47.jpg)
Post a Comment for "41 parts of the animal cells"